The spreading legalization of cannabis has introduced a new alphabet of industry jargon to a growing population of consumers. We’re here to clear the air of confusion, helping the adult user of cannabis products understand the differences between the cannabinoids CBD and THC, so they can make educated and confident decisions.
Start at ground level
Cannabinoids are a group of naturally occurring chemical compounds that bind with receptors in the human body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which regulates many important physiological pathways and systems, including cardiovascular, GI, pain, emotion, hormone, immune and metabolism.
Cannabinoids are produced by the human body (endocannabinoids) as well as the cannabis plant (phytocannabinoids). Regardless of the source, all cannabinoids bind with the ECS receptors throughout the body to produce physiological effects. While there are over 100 different cannabinoids identified in the cannabis plant, Cannabidiol (CBD) and Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are the two most prominent and well-known.
What do they do?
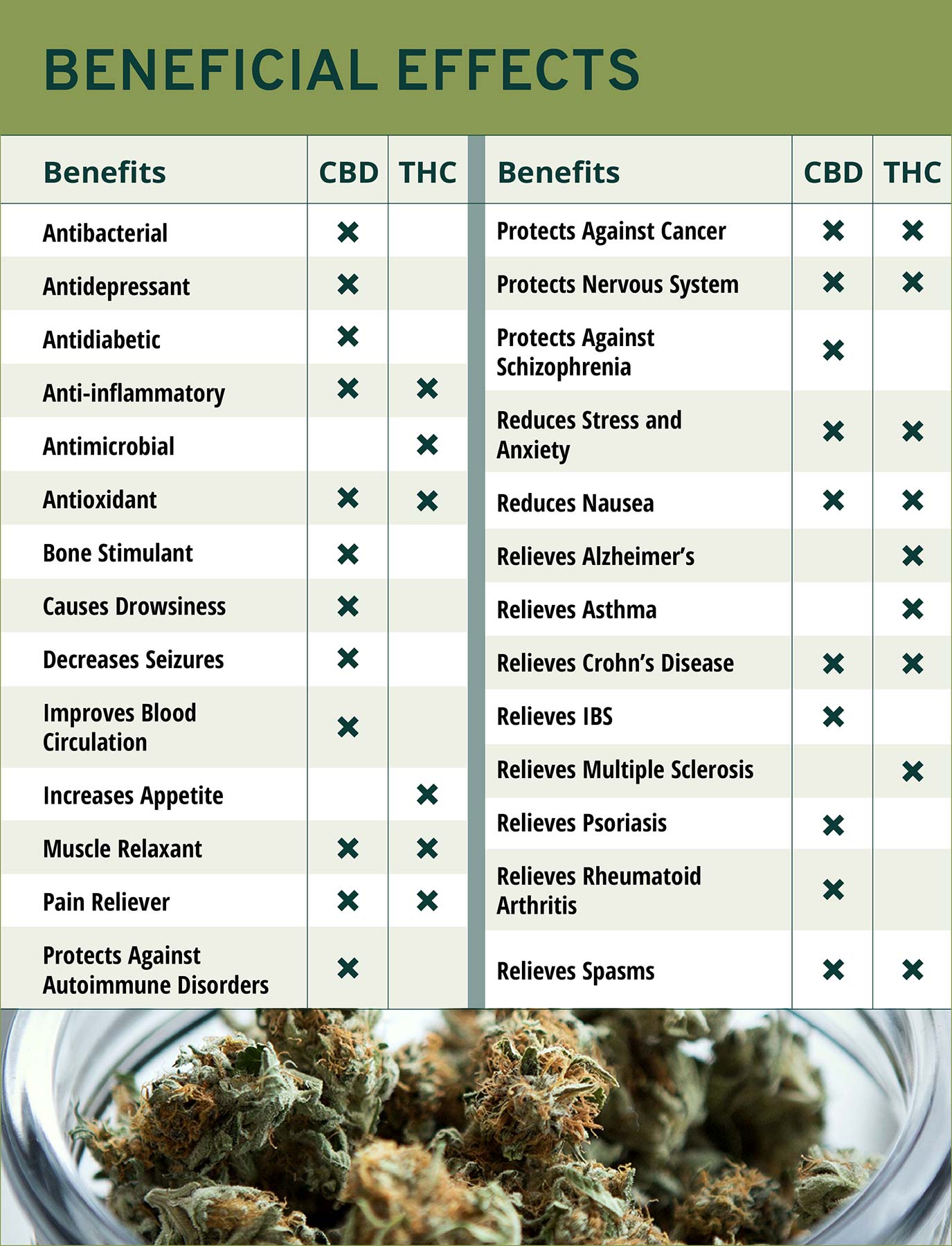
THC is psychoactive, meaning it affects the mind and is responsible for creating the euphoric “high” that is commonly associated with cannabis use. But THC has also been shown to treat pain, insomnia, nausea, and stress disorders. New research is showing promising results in treating a wide variety of health issues including cancer, Alzheimer’s, multiple sclerosis (MS), gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, and even asthma.
CBD is exploding in popularity and is legal in all 50 states. It is not psychoactive and therefore doesn’t get you “high.” Pure CBD—on its own—won’t show up on a drug screen. CBD is a potent anti-inflammatory, which makes it effective at treating many different types of pain. It’s also used to treat epileptic seizures, and current research is showing promising results in treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), cancer, diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), schizophrenia, depression, and a variety of autoimmune disorders and diseases.
Hand in hand
It’s tempting to think that those seeking only the benefits of THC should seek out strains only containing the THC compound, and likewise with CBD. But when THC and CBD are used together, they work synergistically to enhance the effect each has on the body. This is known as the “entourage effect.” It’s not completely understood how this occurs and which other factors may contribute to the effects. But several studies are underway to determine the combination of THC and CBD that produces the best results for various health issues.
Legally-speaking
The two compounds are treated differently under the law. THC is listed in the U.S. Controlled Substances Act and is prohibited under federal law, though more and more states have legalized THC for medical and adult use.
CBD is technically legal under federal law, but only if derived from hemp, which is a cannabis plant that produces very low amounts of THC. The USDA has created a program to allow hemp to be farmed and sold as a commodity, but the FDA has not created regulations that will allow CBD to be used as an ingredient in food, beverages, dietary supplements, animal feed, cosmetics or drugs. With that in mind, beware of CBD products you see in convenience stores or other outlets, as there are no regulations that require testing, so you can’t be sure what is actually in the product.
Today’s adult-use cannabis consumer can find products at local dispensaries that contain a range of THC-to-CBD ratios, as well as those containing only CBD, and a knowledgeable budtender can help you navigate the selection, depending on your own desired results.
LOCATION
40 Westfield Industrial Park
Westfield, MA 01085
Get Directions
CONTACT
(413) 752-2269
Job Opportunities
HOURS
Monday - Saturday 9am–9pm
Sunday 10am–8pm

